DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is a powerhouse email authentication protocol designed to keep your inbox safe from phishing and spoofing attacks. However, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution—it requires a tailored approach to maximize its potential.
At the heart of this customized, personalized solution is a concept called “DMARC alignment.” DMARC alignment (which comes in two flavors: strict and relaxed) plays a pivotal role in determining how rigidly your DMARC policy is enforced.
But what do these terms actually mean? How do they affect the security of your emails? And more importantly, how can you decide which type of alignment is right for your organization?
This article walks you through the complexities around strict and relaxed DMARC alignment, the pros and cons of both modes, and how to choose the best fit for your domain. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or new to the realm of email authentication, we’ve got you covered.
DMARC at a glance
DMARC is an email validation protocol that protects your domain from unauthorized use, such as email spoofing and phishing attacks. It acts as a policy layer on top of SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) to ensure only legitimate messages reach your customers’ inboxes.
However, DMARC does more than just combine these technologies—it adds a crucial layer of policy and reporting capabilities.
At its core, DMARC is about authentication and policy enforcement. It allows domain owners to specify how an email should be authenticated and what should happen if it fails the check. This is where DMARC’s true power lies—in its ability to instruct email receivers on handling unauthenticated messages. Think of it as a bouncer at the door of your email domain, scrutinizing IDs (emails) to decide who gets in and who gets turned away.
Email spoofing and phishing are akin to identity theft, where attackers disguise themselves as trusted entities in your email ecosystem. DMARC effectively counters these attacks by ensuring that the emails sent from your domain are legitimate and authenticated. If an email fails DMARC’s stringent checks, it can be quarantined or rejected, significantly reducing the likelihood of phishing emails reaching their intended targets.
Implementing DMARC fortifies your security and also enhances your domain’s reputation. A domain with a well-configured DMARC policy signals to email receivers that you’re serious about security. This boosts your domain’s credibility and trustworthiness, and a robust DMARC policy can even improve email deliverability.
What is DMARC alignment?
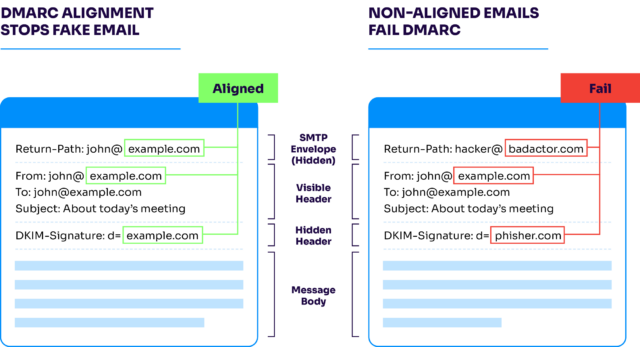
DMARC alignment is a way to ensure that the email sender’s identity is consistent and legitimate across different aspects of the email. It’s about matching the domain in the “From” address of the email (what the recipient sees) with the information authenticated by SPF and/or DKIM.
This alignment is crucial because it prevents bad actors from exploiting mismatches in domain names to slip past email security filters. By verifying that the visible domain matches the authenticated domain, DMARC alignment adds an extra layer of trustworthiness to your emails.
Alignment strengthens your DMARC policy by ensuring the authentication results align with the sender’s stated domain. This alignment is what makes DMARC effective in combating email spoofing and phishing. Without it, malicious senders could easily impersonate domains and deceive recipients.
Strict DMARC alignment vs. relaxed DMARC alignment
DMARC alignment comes in two types: strict and relaxed. Each serves a different purpose, and understanding their nuances is critical to implementing an effective DMARC policy.
-
- Strict Alignment: In strict alignment, an exact match is required between the domains. This means the domain in the “From” address must exactly match the domain validated by SPF and/or DKIM.
-
- Relaxed Alignment: Relaxed alignment, on the other hand, allows for a more lenient matching criterion. It’s satisfied as long as the organizational domains are the same, even if the subdomains differ.
However, it’s a bit more complicated and nuanced than that. Let’s dive deeper into each alignment mode.
Strict DMARC alignment
Strict DMARC alignment is the more rigorous of the two options. It demands an exact match between the domain in the “From” address of the email and the domain authenticated by SPF and/or DKIM. Think of it as a precision lock where only the exact key—the exact domain name—fits. This precision ensures that emails are authenticated most stringently, leaving little room for impersonators to exploit.
Strict alignment is crucial for organizations where security is paramount and the risk of impersonation is high. This includes financial institutions, government entities, and large corporations, especially those that handle sensitive data. In these scenarios, the cost of even a single phishing attack can be substantial, making the strict verification process a necessary safeguard.
-
- Pros: The primary advantage of strict alignment is its enhanced security. It significantly reduces the chances of spoofed or phishing emails getting through, protecting your brand’s integrity and recipients’ trust.
-
- Cons: However, the downside is its inflexibility. It can lead to legitimate emails being rejected or marked as spam if they don’t meet the exact domain match criteria. This can be problematic for organizations with complex email setups or those using various third-party email services.
Relaxed DMARC alignment
Relaxed DMARC alignment offers more flexibility than its strict counterpart. In relaxed alignment, the domain in the “From” address must match the authenticated domain at the organizational level. This means emails sent from a subdomain can still pass DMARC checks even if they don’t match the exact domain used in SPF or DKIM authentication.
Relaxed alignment is suitable for organizations with multiple subdomains or those who use third-party email services for marketing or customer support. It’s ideal for scenarios where strict alignment might be too restrictive and lead to wrongly flagging legitimate emails.
-
- Pros: The main advantage of relaxed alignment is its flexibility. It accommodates a variety of email-sending practices, reducing the likelihood of legitimate emails being rejected.
-
- Cons: The trade-off, however, is that relaxed alignment may allow for a higher risk of spoofed emails slipping through, as it doesn’t require an exact domain match.
Strict vs. relaxed: Side-by-side comparision
Not sure which DMARC alignment mode is suitable for your business? Let’s compare side-by-side and then discuss what to consider when choosing the best alignment fit for your organization.
| Aspect | Strict Alignment | Relaxed Alignment |
| Domain Match | Requires exact domain match in “From” address and SPF/DKIM authentication | Requires match at the organizational level, allowing different subdomains |
| Security Level | Higher, due to stringent authentication | Slightly lower, due to more lenient authentication |
| Best Suited For | Organizations with high security needs like financial institutions, government bodies | Organizations using multiple subdomains or third-party email services |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, may lead to false positives | More flexible, accommodating a range of email practices |
| Risk of Spoofing | Lower, as it leaves little room for impersonation | Slightly higher, due to lenient domain matching criteria |
Here’s what to think about when choosing an alignment mode:
-
- Assess Your Email Practices: Consider the complexity of your email infrastructure. Relaxed alignment might be more practical if you rely heavily on third-party services or have multiple subdomains.
-
- Evaluate Security Needs: For organizations handling sensitive data, the enhanced security of strict alignment could outweigh its lack of flexibility.
-
- Consider Email Volume and Diversity: High email volume with varied sources may favor relaxed alignment to minimize false positives.
The decision between strict and relaxed alignment should be made after thoroughly evaluating your organization’s specific needs, risks, and email practices. Both options have their merits, and understanding these can guide you toward a DMARC policy that bolsters your email authentication while aligning with your operational requirements.
How to choose your DMARC alignment
Ready to implement your chosen DMARC alignment mode? Here’s how to make it happen in your DMARC record:
1. Set your alignment mode in the DMARC record
The DMARC record includes tags that specify your desired policy and alignment mode.
For SPF alignment, use the “aspf” tag:
-
- aspf=s for strict alignment.
-
- aspf=r for relaxed alignment.
For DKIM alignment, use the “adkim” tag:
-
- adkim=s for strict alignment.
-
- adkim=r for relaxed alignment.
For example, a DMARC record with relaxed SPF and strict DKIM alignment would look like:
v=DMARC1; p=reject; aspf=r; adkim=s;2. Implement and test your alignment choice
Monitor the impact after updating your DMARC record with the chosen alignment mode. Begin with a less restrictive policy (p=none or p=quarantine) to observe how your emails are processed without affecting deliverability.

Review DMARC reports to see how emails are aligning under your chosen mode. Look for issues like legitimate emails failing DMARC due to alignment problems.
If legitimate emails are rejected under strict alignment, consider switching to relaxed alignment. Conversely, consider tightening to strict alignment if you observe phishing attempts passing through under relaxed alignment.
3. Monitor and make adjustments
DMARC alignment isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it configuration. Continuously monitor DMARC reports to ensure your alignment mode remains effective and adjust as your email practices evolve, or new threats emerge.
FAQs on DMARC alignment
1. What happens if I don’t set up DMARC alignment correctly?
Incorrect DMARC alignment can lead to legitimate emails being marked as spam or phishing emails slipping through, potentially harming your domain’s reputation and email deliverability.
2. Can I switch between strict and relaxed alignment?
Yes, you can switch between alignment modes by updating the aspf and adkim tags in your DMARC record. Regular monitoring is recommended to assess the impact of any changes.
3. How often should I review my DMARC policy?
We recommend you review your DMARC policy at least quarterly. However, more frequent reviews may be necessary if there are changes in your email-sending practices or if you notice any issues in your DMARC reports.
4. Does DMARC alignment affect email deliverability?
Proper DMARC alignment can improve email deliverability by building trust with email receivers. However, incorrect alignment might lead to legitimate emails being rejected or marked as spam.
Accelerate your journey to DMARC enforcement
DMARC alignment is about more than just protecting your domain from spoofing and phishing—it’s about ensuring the integrity and deliverability of every email you send. The journey to robust DMARC enforcement (while intricate) is essential in the digital age where email communication is foundational.
The first step in that journey is setting up your p=none policy and monitoring your senders. However, this can be time-consuming as you comb through confusing XML reports. Valimail Monitor consumes the reports for you and gives you easy-to-read, digestible reports on your sending services.
The best part is that it’s free.
Get global visibility into all senders using your domain. Expose non-authorized sending services with our unmatched discovery of email services.
Whether you’re an IT professional safeguarding your organization’s email program or an email marketer aiming to maintain your brand’s reputation and trust, we’re here to help. Monitor takes the hard work out of setting up your DMRC policy.
Don’t let the complexities of DMARC alignment hold you back. Start the journey with Monitor and transform your email authentication strategy from a challenge into an asset.